Portal:Asia

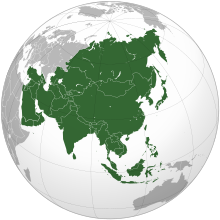 Asia (/ˈeɪʒə/ AY-zhə, UK also /ˈeɪʃə/ AY-shə) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometers, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilizations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. Asia shares the landmass of Eurasia with Europe, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Europe and Africa. In general terms, it is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. It is somewhat arbitrary and has moved since its first conception in classical antiquity. The division of Eurasia into two continents reflects East–West cultural, linguistic, and ethnic differences, some of which vary on a spectrum rather than with a sharp dividing line. A commonly accepted division places Asia to the east of the Suez Canal separating it from Africa; and to the east of the Turkish Straits, the Ural Mountains and Ural River, and to the south of the Caucasus Mountains and the Caspian and Black seas, separating it from Europe. China and India traded places as the largest economies in the world from 1 to 1800 CE. China was a major economic power for much of recorded history, with the highest GDP per capita until 1500. The Silk Road became the main east–west trading route in the Asian hinterlands while the Straits of Malacca stood as a major sea route. Asia has exhibited economic dynamism as well as robust population growth during the 20th century, but overall population growth has since fallen. Asia was the birthplace of most of the world's mainstream religions including Hinduism, Zoroastrianism, Judaism, Jainism, Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism, Christianity, Islam, Sikhism, as well as many other religions. (Full article...) Featured articleSlow lorises are a group of several species of nocturnal strepsirrhine primates that make up the genus Nycticebus. Found in Southeast Asia and bordering areas, they range from Bangladesh and Northeast India in the west to the Sulu Archipelago in the Philippines in the east, and from Yunnan province in China in the north to the island of Java in the south. Although many previous classifications recognized as few as a single all-inclusive species, there are now at least eight that are considered valid: the Sunda slow loris (N. coucang), Bengal slow loris (N. bengalensis), Javan slow loris (N. javanicus), Philippine slow loris (N. menagensis), Bangka slow loris (N. bancanus), Bornean slow loris (N. borneanus), Kayan River slow loris (N. kayan) and Sumatran slow loris (N. hilleri). A ninth species, the pygmy slow loris (X. pygmaeus), was recently moved to the new genus Xanthonycticebus. After the pygmy slow loris, the group's closest relatives are the slender lorises of southern India and Sri Lanka. Their next closest relatives are the African lorisids, the pottos, false pottos, and angwantibos. They are less closely related to the remaining lorisoids (the various types of galago), and more distantly to the lemurs of Madagascar. Their evolutionary history is uncertain since their fossil record is patchy and molecular clock studies have given inconsistent results. Slow lorises have a round head, a narrow snout, large eyes, and a variety of distinctive coloration patterns that are species-dependent. Their arms and legs are nearly equal in length, and their torso is long and flexible, allowing them to twist and extend to nearby branches. The hands and feet of slow lorises have several adaptations that give them a pincer-like grip and enable them to grasp branches for long periods of time. Slow lorises have a toxic bite, a trait rare among mammals and unique among the primates. The toxin is obtained by licking a sweat gland on their arm, and the secretion is activated by mixing with saliva. Their toxic bite, once thought to be primarily a deterrent to predators, has been discovered to be primarily used in disputes within the species. (Full article...)Selected Country Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly in Anatolia in West Asia, with a smaller part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran to the east; Iraq, Syria, and the Mediterranean Sea (and Cyprus) to the south; and the Aegean Sea, Greece, and Bulgaria to the west. Turkey is home to over 85 million people; most are ethnic Turks, while ethnic Kurds are the largest ethnic minority. Officially a secular state, Turkey has a Muslim-majority population. Ankara is Turkey's capital and second-largest city. Istanbul is its largest city, and its economic and financial center, as well as the largest city in Europe. Other major cities include İzmir, Bursa and Antalya. Human habitation began in the Late Paleolithic. Home to important Neolithic sites like Göbekli Tepe and some of the earliest farming areas, present-day Turkey was inhabited by various ancient peoples. Hattians were assimilated by the Anatolian peoples. Classical Anatolia transitioned into cultural Hellenization following the conquests of Alexander the Great; Hellenization continued during the Roman and Byzantine eras. The Seljuk Turks began migrating into Anatolia in the 11th century, starting the Turkification process. The Seljuk Sultanate of Rum ruled Anatolia until the Mongol invasion in 1243, when it disintegrated into Turkish principalities. Beginning in 1299, the Ottomans united the principalities and expanded; Mehmed II conquered Istanbul in 1453. During the reigns of Selim I and Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire became a global power. From 1789 onwards, the empire saw major transformation, reforms, and centralization while its territory declined. (Full article...)Featured biographySonam Kapoor Ahuja (pronounced [soːnəm kəˈpuːr]; born 9 June 1985) is an Indian actress who works in Hindi films. She has received several awards, including a National Film Award and a Filmfare Award. One of the highest-paid actresses in India as of 2018, Kapoor appeared in Forbes India's Celebrity 100 list from 2012 to 2016. Kapoor, the daughter of actor Anil Kapoor, began her career as an assistant director on filmmaker Sanjay Leela Bhansali's 2005 film Black. She made her acting debut in Bhansali's romantic drama Saawariya (2007), a box office flop, and had her first commercial success with the romantic comedy I Hate Luv Storys (2010). This was followed by a series of commercial failures and repetitive roles, which garnered her negative reviews. The 2013 box office hit Raanjhanaa marked a turning point in Kapoor's career, garnering her praise and Best Actress nominations at several award ceremonies. (Full article...)General imagesThe following are images from various Asia-related articles on Wikipedia. Featured pictureDid you know...
Updated: 6:33, 14 February 2024 In the news
Related portalsMajor Religions in Asia Middle East Central Asia and Surroundings Indian Subcontinent Southeast Asia East Asia Selected panorama
Nanga Parbat is the ninth highest mountain on Earth, the second highest mountain in Pakistan and among the eight-thousanders with a summit elevation of 8,126 meters (26,660 ft). TopicsCategoriesAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
More portalsShortcuts to this page: Asia portal • P:ASIA Purge server cache |































































































